Updated:
VGA Video Signal Format and Timing Specifications
VGA Video Signal Format
A color VGA video signal is composed by 5 different signals: two synchronization signals (HSYNC and VSYNC) and three color signals (R, G, B)
- HSYNC
- Horizontal sync. Make electron beam restart at next screen's scanline (starts a new line).
- VSYNC
- Vertical sync. Make electron beam restart at first screen's scanline (starts a new frame).
- R
- Red intensity.
- G
- Green intensity.
- B
- Blue intensity.
HSYNC and VSYNC signals determines the screen resolution (for example 640x480) whereas the colour of every pixel is determined by the value of R, G and B signal. Each color is a combination of the 3 primary colours R, G and B.
HSYNC and VSYNC signals are a train of squared pulses of +5V (+3.3V serves too) whereas RGB signals take values in a continuous (analog) voltage range from +0V (absolutely dark) to +0.7V (maximum brightness). Each of this 3 signals controls a electron gun that makes the screen's phosphor bright a basic colour (R, G or B) in a pixel. Any colour is the visual mixture of different levels of brightness of the 3 primary colours.
A single dot of colour on a video monitor doesn’t impart much information. A horizontal line of pixels carries a bit more information. But a frame composed of multiple lines can present an image on the monitor screen. In a 640x480 mode, for example, a frame of VGA video has 480 lines and each line '''usually''' contains 640 pixels (see later).
In order to paint a frame, there are deflection circuits in the monitor that move the electrons emitted from the guns both left-to-right and top-to-bottom across the screen. These deflection circuits require two synchronization signals in order to start and stop the deflection circuits at the right times so that a line of pixels is painted across the monitor and the lines stack up from the top to the bottom to form an image. The timing for the VGA synchronization signals is shown in Figure 2.
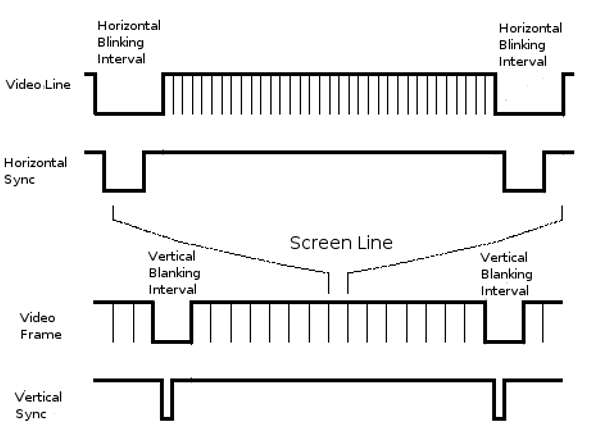
- Pulses on HSYNC signal mark the start and end of a line and ensure that the monitor displays the pixels between the left and right edges of the visible screen area.
- Pulses on VSYNC signal mark the start and end of a frame made up of video lines and ensure that the monitor displays the lines between the top and bottom edges of the visible monitor screen.
- As you may have guessed, the horizontal resolution of each line '''is not actually determined''' and could be anything, this resolution is determined typically by a '''pixel clock'''. Every rising edge of the pixel clock marks the start of a new pixel.
Video Modes and Their Signal Timings
The following table shows the time restrictions that video signal must obey in order to the monitor can synchronize and displays the image correctly (without blinks). The pixel clock frequency is only orientative, when designing a video hardware, you can use the pixel clock frequency that you want, the only important thing is that the video signal fits with the time restrictions (measures A, B, C, etc).
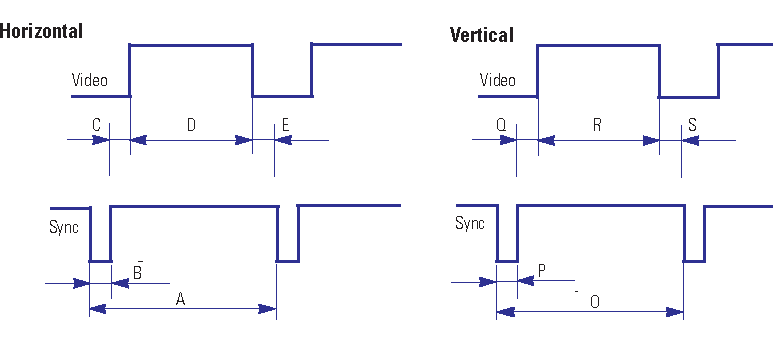
| IBM | VESA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Unit | 640x480 60Hz |
720x400 70Hz |
640x480 75Hz |
640x480 85Hz |
800x600 75Hz |
800x600 85Hz |
1024x768 75Hz |
1024x768 85Hz |
| F_HSYNC | kHz | 31.469 | 31.469 | 37.500 | 43.269 | 46.875 | 53.674 | 60.023 | 68.677 |
| A | us | 31.778 | 31.777 | 26.667 | 23.111 | 21.333 | 18.631 | 16.660 | 14.561 |
| B | us | 3.813 | 3.813 | 2.032 | 1.556 | 1.616 | 1.138 | 1.219 | 1.016 |
| C | us | 1.907 | 1.907 | 3.810 | 2.222 | 3.232 | 2.702 | 2.235 | 2.201 |
| D | us | 25.422 | 25.422 | 20.317 | 17.778 | 16.162 | 14.222 | 13.003 | 10.836 |
| E | us | 0.636 | 0.636 | 0.508 | 1.558 | 0.323 | 0.589 | 0.203 | 0.508 |
| F_VSYNC | Hz | 59.940 | 70.087 | 75.000 | 85.008 | 75.000 | 85.061 | 75.029 | 84.997 |
| O | ms | 16.683 | 14.268 | 13.333 | 11.764 | 13.333 | 11.758 | 13.328 | 11.765 |
| P | ms | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.080 | 0.671 | 0.064 | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.044 |
| Q | ms | 1.048 | 1.080 | 0.427 | 0.578 | 0.448 | 0.503 | 0.466 | 0.524 |
| R | ms | 15.253 | 12.711 | 12.800 | 11.093 | 12.800 | 11.179 | 12.795 | 11.183 |
| S | ms | 0.318 | 0.413 | 0.027 | 0.023 | 0.021 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.015 |
| Pixel Clock | MHz | 25.175 | 28.322 | 31.500 | 36.000 | 49.500 | 56.250 | 78.750 | 94.500 |
| Polarity HSYNC | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | Pos | Pos | Pos | Pos | |
| Polarity VSYNC | Neg | Pos | Neg | Neg | Pos | Pos | Pos | Pos | |
VGA Connector
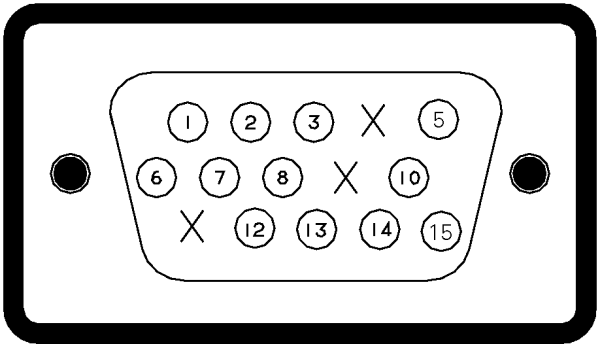

| Pin | PC (DB15 connector) | Macintosh |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Red | GND-R |
| 02 | Green | Ref |
| 03 | Blue | H/V-Sync (not separate sync) |
| 04 | NC | Sense 0 |
| 05 | DDC Return | Green |
| 06 | GND-R | GND-G |
| 07 | GND-G | Sense 1 |
| 08 | GND-B | Reserved |
| 09 | NC | Blue |
| 10 | GND-Sync/Self Raster | Sense 2 |
| 11 | NC | GND |
| 12 | DDC Data | V-Sync |
| 13 | H-Sync | GND-B |
| 14 | V-Sync | GND |
| 15 | DDC Clock | H-Sync |